
Digital governance towards a new era of smart city and public safety

How can cities use big data and related technologies to make better decisions about public safety, defense and city operations? And what role does digital governance play?
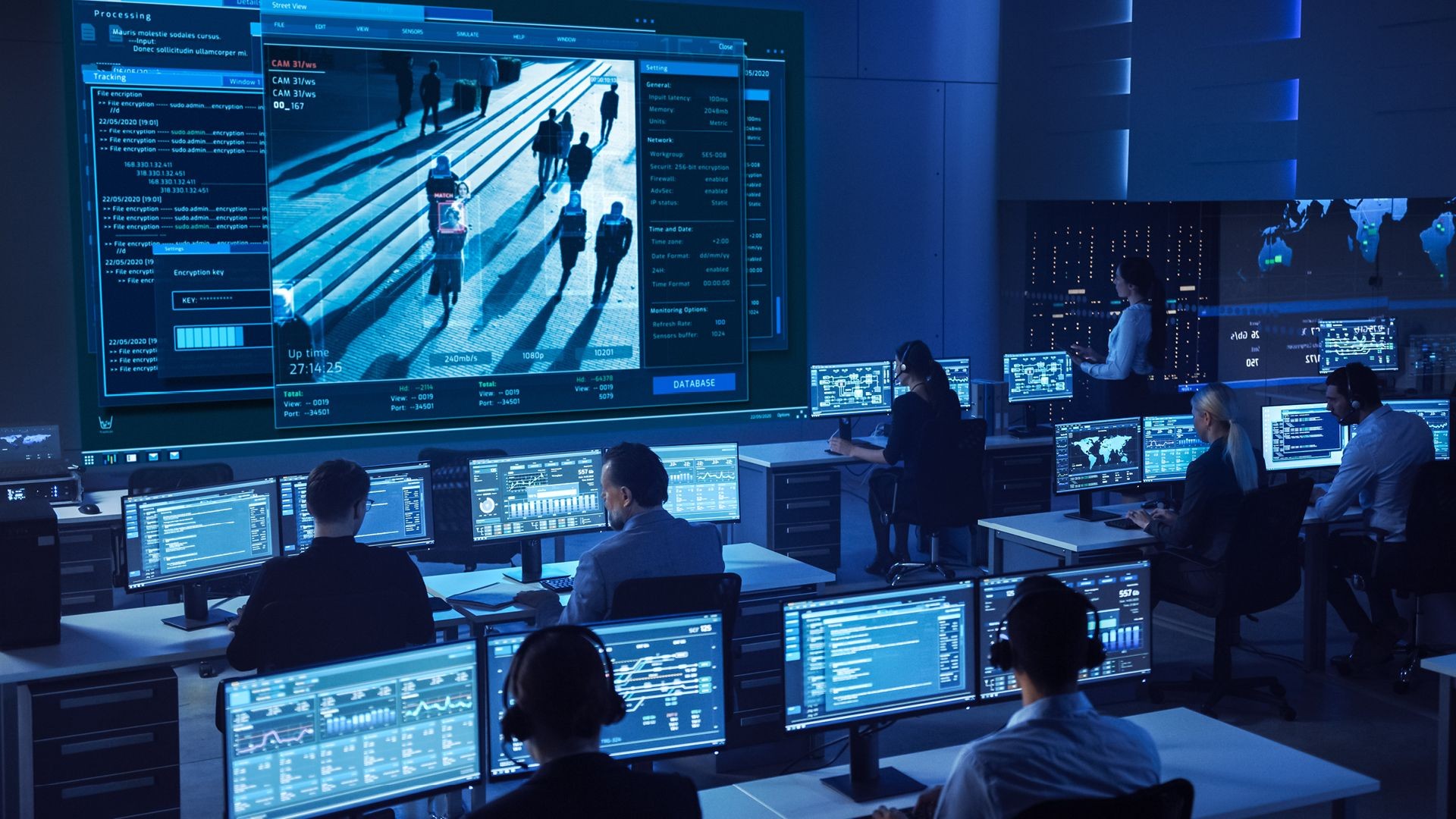
When it comes to public safety in our cities, the integration of digital technology in smart city planning is becoming an increasingly important factor. It enables data-driven decision-making, improves surveillance, streamlines emergency response, and enhances overall community safety, enabling the cognitive cities of tomorrow to provide a safer environment for all.
Technologies such as predictive analytics, big data, IoT, cybersecurity protocols and AI, are being employed in the realm of public safety and defense to enable better community engagement and data-driven decision-making, which make the cities of the future more resilient with a high disaster preparedness.
But with all these great technological strides, caution must be taken in the implementation of technologies as it also raises important issues regarding privacy and security, which must be addressed to maintain the trust and well-being of the city's residents. Guardrails in the use of digital technologies for public safety should be firmly set to ensure data is accurate, sovereign, maintained, and utilized ethically, with utmost care in complying with privacy laws and ED&I policies.
This is where digital governance plays a critical role — ensuring that public safety measures are effective, inclusive, and equitable in smart cities. By encompassing a set of policies, practices, and technologies, it helps guide the use of digital resources and data in a way that serves the public interest.
Big data and public safety
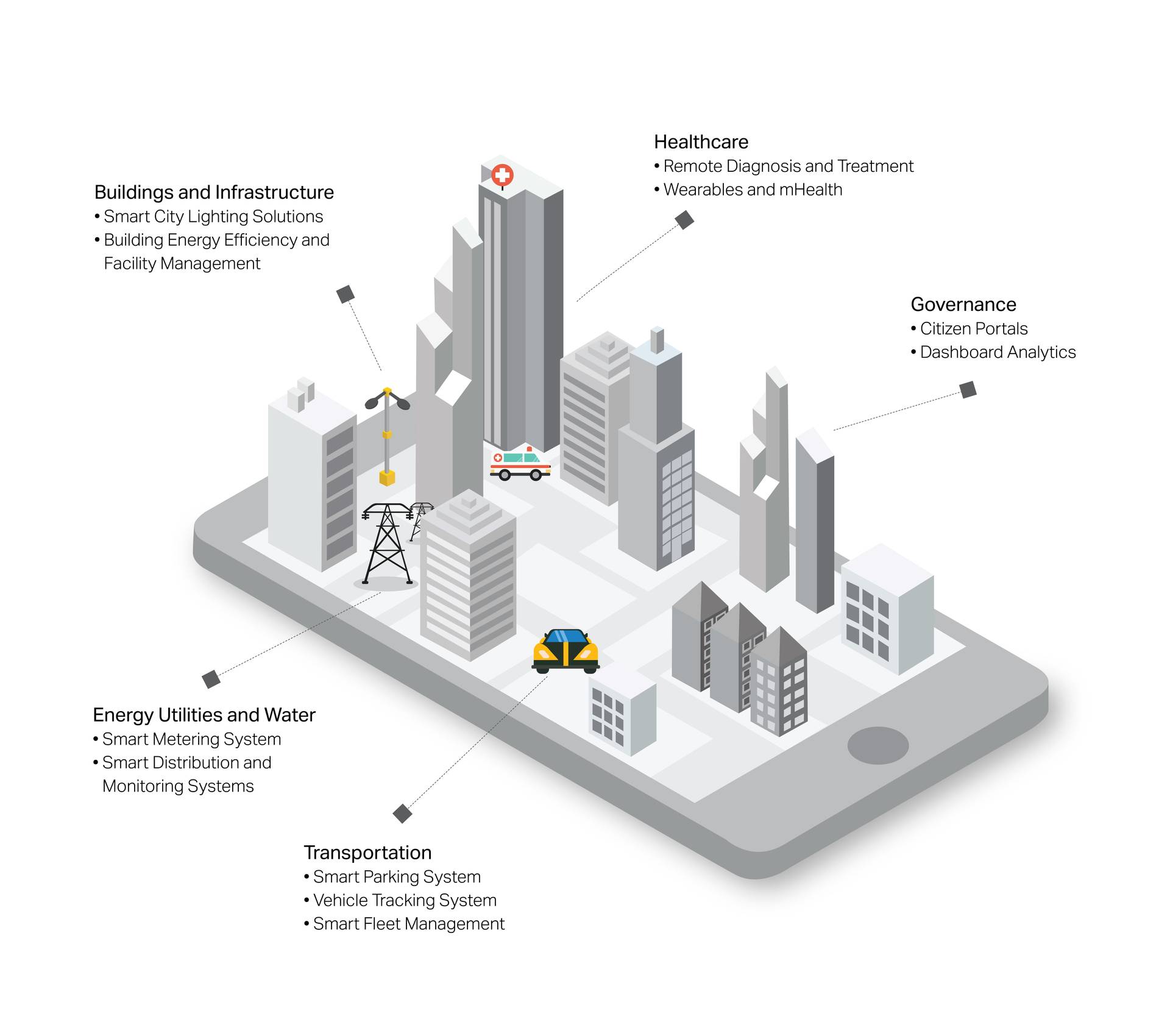
In an effort to prepare the cities of the world in being smarter and more cognitive, it is essential to leverage and harness big data and related technologies to make better decisions about public safety
and city operations. Being predictive is key to success of any safety and security measure. Leveraging predictive analytics allows cities to foresee when and where incidents such as traffic accidents, crimes, or environmental issues are likely to occur. Predictive models also enable proactive resource allocation and improved emergency response.
The use cases vary but point to the same benefit, which is the enablement of preventive security and safety via state-of-the-art data capture using drones, sensors and IoT, to be analyzed and leveraged in predictive data analysis systems.
Leveraging big data and related technologies to improve decision-making on public safety and city operations
Notable examples include:
− Healthcare management: When faced with health crises, big data can be used to track the spread of diseases, monitor healthcare resources, and enforce safety measures. This is especially relevant in managing pandemics, where data-driven decisions can help protect public health. During the pandemic in 2020, data analytics for case management and proactive response was paramount in controlling disease spread.
− Infrastructure maintenance: Big data can be used to monitor the condition of infrastructure, such as roads, bridges and public buildings. By analyzing data on wear and tear, cities can schedule maintenance and repairs before accidents or disruptions occur. With next level asset management, predictive maintenance is closer to a reality.
− Waste management: IoT sensors and data analysis can optimize waste collection routes, reducing the environmental impact and traffic congestion associated with waste removal. In today’s world, the presence of smart bins in emerging cities is a step towards an enhanced smart city. Smart bins are of varying types but operate with a similar premise of having sensors and compactors within the typical neighborhood bin, by which the compactor would compact the trash increasing the bin’s capacity five times. The sensor sends a signal to a control room upon the bin reaching capacity, which then results in an efficient dispatch system for waste removal.
− Transport: Transport authorities today are looking at different technologies to be leveraged for multiple use cases, some of which would be the use of IoT sensors, cameras and GPS data to provide real-time information on traffic flow, congestion and accidents. Big data analytics can process this information to optimize traffic signal timings, reroute traffic in case of accidents, and provide commuters with real-time traffic updates through navigation apps. This reduces traffic congestion and improves road safety.
The application of digital governance
With the integration of digital technologies into smart cities transforming the landscape of public safety, the importance of robust digital governance, privacy protections, and cybersecurity measures is paramount. Striking a balance between harnessing the potential of digital innovation and safeguarding individual rights and community well-being is essential.
Digital governance facilitates data sharing and integration among various government agencies, public safety organizations and stakeholders. This enables a holistic view of public safety data, making it easier to identify trends, respond to emergencies and allocate resources effectively. For example, sharing data between law enforcement, emergency services and public health agencies can help in managing public safety during a pandemic or natural disaster. However, it is always imperative to ensure this abides by transparent methods of data sharing and compliance with privacy and data ownership laws in the city.
Transparency in digital governance means making relevant data and decision-making processes accessible to the public. When public safety data and policies are transparent, residents can better understand how their safety is being managed. This transparency builds trust and encourages collaboration between city authorities and citizens.
This is why protecting individual privacy rights is such a key aspect of digital governance, particularly when collecting and sharing data related to public safety. Privacy regulations and practices ensure that personal data is handled responsibly, reducing the risk of privacy breaches or misuse of personal information.
As such, digital governance should aim to establish accountability mechanisms, ensuring that public safety measures are carried out responsibly and ethically. In the context of public safety, this means
that actions and decisions of law enforcement, emergency services and city officials are subject to scrutiny, reducing the likelihood of misuse of power and discrimination.
With proper collaboration and participation in public safety decision- making, digital governance should also address issues of equity and inclusivity by ensuring that public safety measures are accessible
to all residents, regardless of their background or abilities. For example, ensuring that digital emergency alerts are accessible to people with disabilities or those who speak languages other than the majority language. It is also imperative that residents feel involved via providing feedback, reporting incidents and suggesting improvements through digital channels.
Finally, when it comes to digital governance, public-safety bodies have responsibility of ensuring the following:
− Data quality and accuracy: Governance frameworks ensure that data used for public safety measures are accurate and of high quality. Inaccurate data can lead to ineffective decision-making and may disproportionately impact vulnerable communities.
− Ethical use of technology: Digital governance helps establish ethical guidelines for the use of emerging technologies, such as AI and facial recognition, in public safety. It ensures that these technologies are used in ways that respect individual rights and do not perpetuate biases or discrimination.
− Cybersecurity and resilience: Governance practices include cybersecurity measures to protect public safety data from cyber threats. By safeguarding data integrity, cities can ensure that public safety measures are not compromised by malicious actors.
− Data ownership and control: Governance frameworks address issues of data ownership and control. Citizens should have some degree of control over their personal data and an understanding of how it is used in public safety efforts.
Digital governance, when implemented effectively, ensures that public safety measures are not only efficient and effective but also considerate of inclusivity, equity, and individual rights. It fosters a collaborative environment where residents and city authorities work together to create a safer and more equitable urban environment.
Case Study: Predictive analytics reduce risks in Dubai
The use of predictive analytics to help generate risk forecasts from historical data was used several years ago as part of work done for the government authorities in Dubai, UAE.
The project team used data analytics from GPS coordinates of traffic accidents reported on the Dubai Police App — which provides services in seven different languages to accommodate the diverse demography of the city — to identify patterns and trends related to public safety and city operations.
By conducting a geo-spatial analysis of historical traffic accident data along with its impact and severity, the map is then superimposed with that data, giving transport authorities insights on the problematic areas to help drive their traffic solutions. Data was filtered by severity and root cause to further understand the issues.
A similar process and outcomes were seen in a different use case — emergency response. By analyzing data on the location and nature of emergencies, as well as real-time traffic and weather conditions, authorities optimized the dispatch of emergency services. Mobile apps and communication systems also allowed citizens to report incidents and receive emergency alerts, improving overall public safety.
In addition, the Dubai Civil Defence launched the Hassantuk App to enable residents of the city to identify the category/type of residence where smart fire alarm systems installed by developers are used to enhance emergency response in case of fire. This enabled a paradigm change, with the Dubai Civil Defence embracing the state- of-the-art Smart Monitoring System to monitor fire alarm and firefighting systems in real-time for immediate dispatch during an emergency.